Discover Australia's Finest
Explore the latest news, insights, and stories from down under.
Nuke Like a Pro: Secrets They Don't Want You to Know
Unlock the hidden secrets to mastering nuclear strategy! Learn insider tips and techniques they don’t want you to discover.
Top 10 Nuclear Survival Tips: What You Need to Know
In the event of a nuclear emergency, knowing how to protect yourself and your loved ones is crucial. Here are the Top 10 Nuclear Survival Tips that everyone should be aware of:
- Stay informed through reliable news sources and government announcements.
- Identify your nearest fallout shelter and understand the best routes to get there.
- Keep a well-stocked emergency kit that includes food, water, and medical supplies.
- Understand the shielding principles—thicker walls and basements offer better protection against radiation.
- Learn about the duck and cover method to protect yourself in case of an explosion.
Additionally, preparation is key. Make sure to:
- Have a family communication plan in place for emergencies.
- Know how to tune into emergency broadcasts on a battery-powered radio.
- Research local resources and support groups for nuclear preparedness.
- Practice drills so everyone knows what to do when disaster strikes.
- Stay calm and focused; clear thinking will be essential during a crisis.
By following these Nuclear Survival Tips, you'll be better equipped to handle a nuclear incident and protect yourself and your family.
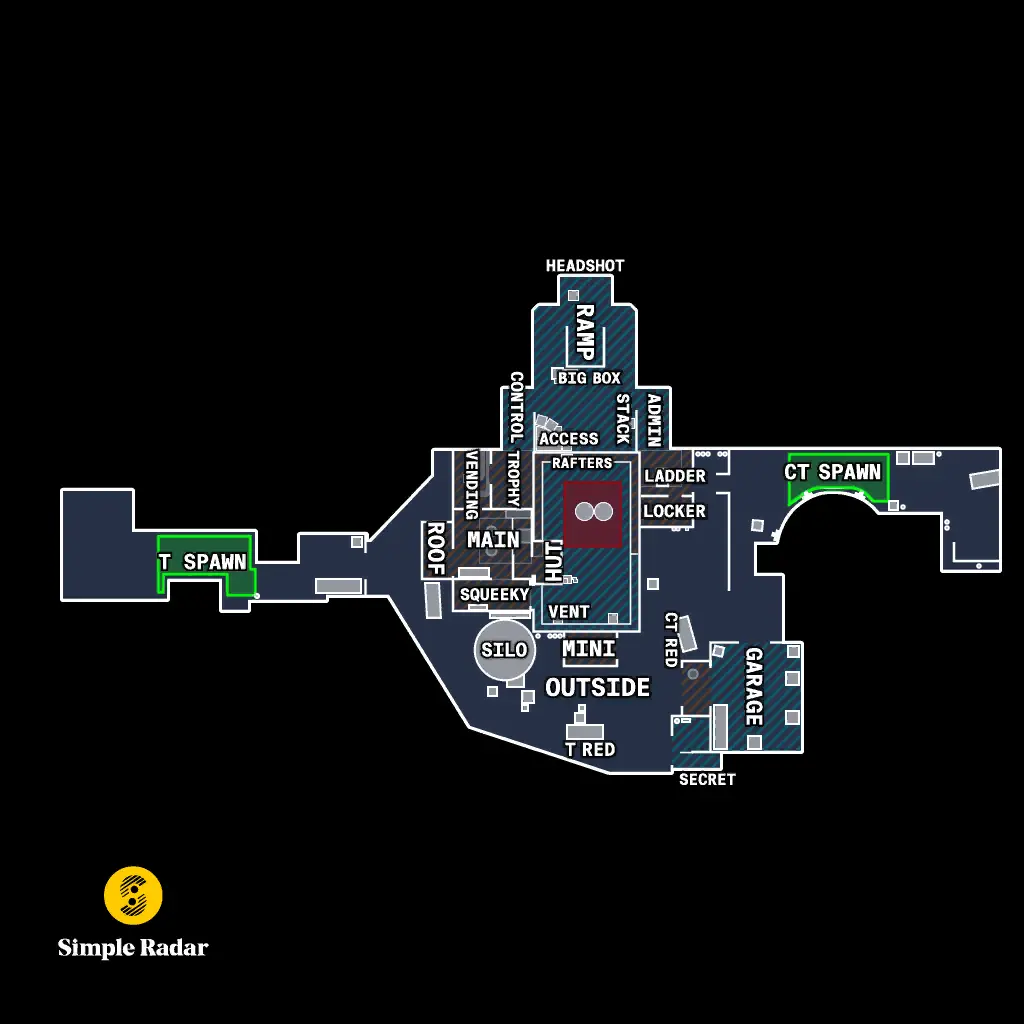
Counter-Strike is a popular tactical first-person shooter game that has captivated gamers for years. One of the exciting features players often look for is the cs2 infinite time command, which allows for endless gameplay scenarios and practice opportunities.
The Science Behind Nuclear Reactions: Simplifying Complex Concepts
Nuclear reactions are fundamental processes that occur at the atomic level, involving changes in the nucleus of an atom. These reactions can be broadly classified into two categories: fission and fusion. In fission, a large atomic nucleus splits into smaller fragments, releasing a significant amount of energy in the form of heat and radiation. This is the principle behind nuclear power plants, where controlled fission reactions are harnessed to generate electricity. On the other hand, fusion occurs when two light atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, a process that powers the sun and other stars. Understanding these two types of nuclear reactions provides a framework for exploring their applications and implications in energy production and beyond.
The science behind nuclear reactions is rooted in the principles of nuclear physics. At the core of these reactions is the strong nuclear force, which binds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus, overcoming the repulsive electromagnetic force between positively charged protons. The various isotopes of elements, each containing a different number of neutrons, play a crucial role in determining how these reactions occur. For example, isotopes like Uranium-235 and Plutonium-239 are favorable for fission, while isotopes like Deuterium and Tritium are needed for fusion. As we delve deeper into the subject, it becomes evident that the applications of these reactions extend far beyond energy, impacting various fields such as medicine, security, and environmental science.
Common Misconceptions About Nuclear War: Debunking Myths
Nuclear war is often shrouded in fear and misunderstanding, leading to several common misconceptions. One prevalent myth is that a nuclear conflict would instantly result in the end of human civilization. While the catastrophic consequences of a nuclear war are undeniable, many experts argue that the aftermath would not necessarily lead to immediate extinction. Instead, it could result in a prolonged crisis marked by geopolitical turmoil, long-term health effects, and environmental devastation. Understanding the complexities of nuclear warfare helps clarify that while the risks are tremendous, the narrative often oversimplifies the situation.
Another significant myth is that the nuclear arsenals of superpowers will lead to an inevitable conflict. In reality, many nations with nuclear capabilities have established robust diplomatic channels and deterrence strategies that prioritize stability and peace. This principle, known as Mutually Assured Destruction (MAD), suggests that the existence of these weapons may actually deter war rather than provoke it. By demystifying these beliefs, we can foster a more informed dialogue about nuclear disarmament and global security.